Tech hiring in 2024 emerged as a pivotal topic of discussion, driven by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence, the global workforce reshuffling, and economic adjustments. As organizations adapted to new tools like Generative AI (GenAI), redefined expectations for talent, and navigated challenges, the year provided significant learning opportunities. Below is a detailed review, expanding on successes, failures, and key insights that shaped the industry.
What Went Right in 2024?
1. Adoption of Generative AI in Recruitment
Generative AI tools revolutionized how companies approached Tech Hiring:
- Resume Screening: AI identified and shortlisted candidates at a speed 10x faster than manual processes, with 95% accuracy.
- Interview Automation: AI-driven chatbots conducted initial interviews, assessing candidates’ technical and cultural fit.
- Job Description Customization: Companies like Google and Meta used AI tools to craft personalized job descriptions based on market trends and candidate data.
This not only saved time but reduced biases. 35% of HR professionals reported that AI-driven hiring improved diversity in their teams by surfacing non-traditional candidates.
2. Skills Over Degrees
With the rise of GenAI and other advanced technologies, employers prioritized skills over formal education:
- Coding Bootcamps on the Rise: Enrollments in platforms like Lambda School and Codecademy surged by 30%.
- Practical Assessments: Over 70% of companies conducted task-based evaluations instead of focusing solely on resumes.
This approach unlocked talent from unconventional backgrounds and helped address skill shortages.
3. Remote Work Drives Globalization
Remote and hybrid work models opened doors to international talent:
- 60% of tech roles were offered as remote positions, compared to 50% in 2023.
- Emerging tech hubs in LATAM, Southeast Asia, and Eastern Europe became popular hiring pools.
Organizations like Microsoft expanded hiring efforts in underrepresented regions, boosting workforce diversity by 18% YoY.
Market Landscape Shifts Across the Year (Jan–Dec 2024)
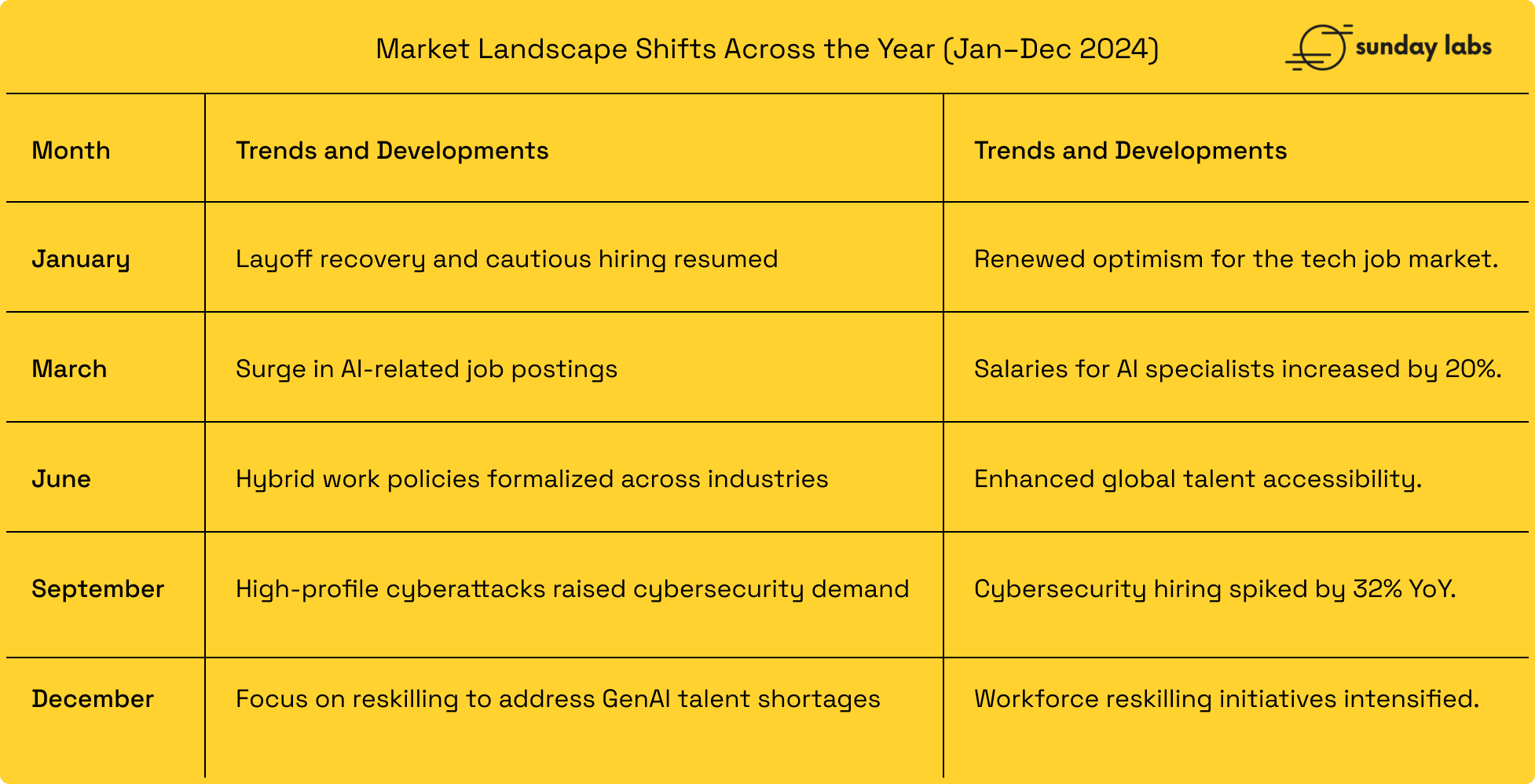
What Went Wrong in 2024?
1. The Persistent Skills Gap
Despite advancements, a widening skills gap hampered progress:
- 69% of tech leaders reported prolonged vacancies in AI and cloud-related roles, with senior positions remaining open for an average of 6 months.
- Fields like multi-cloud management and blockchain struggled to find talent with adequate hands-on experience.
2. Burnout and Attrition
Hybrid work blurred boundaries between personal and professional lives:
- Attrition rates in cybersecurity roles increased by 15% YoY due to excessive workloads from frequent cyberattacks.
- Even in flexible work environments, 43% of employees reported challenges maintaining work-life balance.
3. Ethical Concerns in AI-Driven Hiring
The reliance on AI introduced questions about fairness and bias:
- 25% of candidates raised concerns about the lack of transparency in AI assessments.
- Reports surfaced of AI tools unintentionally excluding candidates due to poorly optimized training data.
Role of Generative AI in Tech Hiring
Generative AI revolutionized hiring in 2024, transforming how companies identify, evaluate, and engage talent by streamlining processes, enhancing decisions, and improving candidate experiences.
1. Automating Resume Screening and Candidate Matching
Generative AI-powered tools have redefined the tedious task of resume screening. These systems go beyond keyword matching to analyze candidates’ skills, experiences, and potential fit for a role. With capabilities like:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interpret complex resumes.
- Machine Learning (ML) to refine matching algorithms based on past hiring patterns.
- Intelligent scoring systems to rank candidates based on role-specific criteria.
Hiring managers can now focus on engaging with top-tier candidates rather than sifting through volumes of resumes.
2. Personalizing Job Descriptions and Outreach
AI has transformed job postings and candidate engagement by enabling hyper-personalization. Generative AI tools can:
- Create tailored job descriptions that highlight company values and role expectations, appealing to specific candidate profiles.
- Generate customized email outreach campaigns, increasing response rates from potential hires.
- Craft compelling LinkedIn posts and ads that attract talent with diverse skill sets.
By personalizing communication, companies enhance their employer brand and foster better connections with job seekers
3. Conducting AI-Driven Preliminary Interviews
Generative AI chatbots have become the first point of interaction for many candidates. These bots simulate human-like conversations, conduct initial screenings, and assess candidates’ qualifications through:
- Conversational AI: Asking relevant questions about skills, experience, and role preferences.
- Sentiment analysis: Gauging enthusiasm and engagement during interactions.
- Real-time feedback: Providing insights to candidates on their responses and next steps.
This approach saves time for recruiters while ensuring every candidate feels engaged and valued.
4. Reducing Bias in Hiring Decisions
One of the most significant benefits of generative AI is its ability to minimize unconscious bias. AI systems, when properly trained, focus on objective criteria, such as skills and qualifications, rather than subjective factors like names, gender, or educational background. By ensuring a fair evaluation process, generative AI helps organizations build diverse and inclusive teams.
5. Enhancing Skill Assessments with AI-Generated Tests
Generative AI has elevated technical and soft skill assessments by creating dynamic, role-specific tests. For example:
- Coding challenges tailored to the hiring company’s tech stack.
- Problem-solving scenarios generated in real-time to test critical thinking.
- Simulated job tasks for UX designers, data analysts, and other specialized roles.
These assessments provide a clearer picture of candidates’ abilities, enabling data-driven hiring decision
6. Streamlining Onboarding and Training
Generative AI doesn’t stop at hiring; it also plays a crucial role in onboarding new employees. AI-driven platforms can:
- Generate personalized onboarding plans based on an employee’s role and skill level.
- Create custom learning modules for upskilling in specific technologies or methodologies.
- Simulate real-world scenarios for hands-on training in virtual environments.
This ensures a seamless transition for new hires and accelerates their productivity.
7. Driving Cost and Time Efficiency
Generative AI significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional recruitment processes. From automating repetitive tasks to improving the accuracy of candidate shortlisting, AI helps companies fill roles faster while maintaining high-quality hires. For startups and enterprises alike, this efficiency translates to a competitive edge in securing top talent.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While generative AI offers numerous benefits, its implementation comes with challenges:
- Data privacy concerns: Ensuring candidate information is handled securely.
- Potential algorithmic biases: AI models must be carefully trained to avoid reinforcing existing biases.
- Human oversight: Balancing automation with human judgment is crucial to maintain a personal touch in recruitment.
Organizations that navigate these challenges responsibly can maximize the potential of generative AI in hiring.
Demand for Niche Tech Skills: A Closer Look in 2024
The rapid evolution of technology in 2024 has intensified the demand for niche skills across various domains. As organizations adopt new technologies to stay competitive, they are on the lookout for specialists who can drive innovation and efficiency. Below, we dive deeper into the top niche skills that defined this year’s hiring landscape and the factors contributing to their demand.
1. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
AI and ML continued to dominate the tech hiring market in 2024. Organizations sought experts who could develop and deploy intelligent algorithms to automate processes, analyze big data, and provide actionable insights. The surge in generative AI applications, such as AI content creation and conversational bots, further amplified the demand for:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) specialists for chatbots and voice assistants.
- Computer vision engineers for AI in healthcare, automotive, and surveillance.
- MLOps engineers to streamline AI model deployment and monitoring.
These roles required expertise in Python, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and cloud platforms, making professionals with such skills highly coveted.
2. Blockchain Development
The resurgence of blockchain technology, driven by decentralized finance (DeFi) and the growing popularity of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), created a strong demand for blockchain developers. Beyond cryptocurrency, companies explored blockchain applications in supply chain management, healthcare, and identity verification.
Key skills in demand included:
- Proficiency in blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Solana, and Hyperledger.
- Knowledge of smart contract programming using Solidity or Rust.
- Understanding of cryptography and consensus algorithms.
Blockchain experts were not only required in startups but also in established enterprises looking to integrate decentralized systems.
3. Cloud Computing
With an increasing number of businesses migrating to the cloud, professionals skilled in cloud architecture and management were in high demand. Companies focused on optimizing cloud infrastructures for cost-efficiency and scalability, making skills in the following areas essential:
- Expertise in Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Knowledge of Kubernetes and Docker for container orchestration.
- Experience with serverless computing and Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform.
Specialists with certifications like AWS Certified Solutions Architect or Google Cloud Professional Architect stood out in the competitive hiring market.
4. Cybersecurity
The rise in cyber threats and data breaches made cybersecurity one of the most critical fields in 2024. Companies prioritized hiring professionals to protect sensitive data, prevent ransomware attacks, and ensure compliance with stringent regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
In-demand cybersecurity roles included:
- Penetration testers and ethical hackers to identify vulnerabilities.
- Security analysts for real-time threat monitoring and response.
- Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) to lead enterprise-wide security initiatives.
Skills in ethical hacking tools, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, and incident response frameworks were particularly sought after.
5. DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE)
The demand for seamless integration of development and operations grew as organizations emphasized faster product delivery and operational efficiency. DevOps professionals were key to bridging this gap, with expertise required in:
- CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins, GitLab, and CircleCI.
- Monitoring systems like Prometheus and Grafana for SRE roles.
- Scripting languages like Bash, Python, and Go for automation.
DevOps and SRE professionals played a pivotal role in maintaining system reliability while accelerating development cycles.
6. Data Science and Big Data Analytics
Data remains the lifeblood of modern businesses, and professionals skilled in extracting actionable insights from vast datasets were in high demand. Hiring trends in this domain focused on:
- Data scientists with a strong grasp of statistical analysis and machine learning.
- Data engineers who could design and maintain scalable data pipelines.
- Knowledge of tools like Apache Spark, Hadoop, and Snowflake for handling big data.
Industries such as healthcare, e-commerce, and finance heavily relied on data analytics for strategic decision-making.
Why Are Niche Tech Skills in High Demand?
The demand for niche skills is driven by several factors:
- Technological Innovation: Emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT require specialists to implement and scale solutions.
- Industry-Specific Applications: Different industries are leveraging these technologies to solve unique challenges, creating specialized roles.
- Skill Gaps: The rapid pace of technological advancement often outpaces traditional education, resulting in a scarcity of professionals with these skills.
- Global Digital Transformation: Businesses across the globe are digitizing their operations, further fueling the need for expertise in advanced technologies.
Salary Trends and Data Insights
As the tech industry evolved in 2024, salary trends reflected the shifting priorities of companies and the growing demand for specialized skills. Here’s a breakdown of the key insights from 2024 and what to expect as we approach 2025.
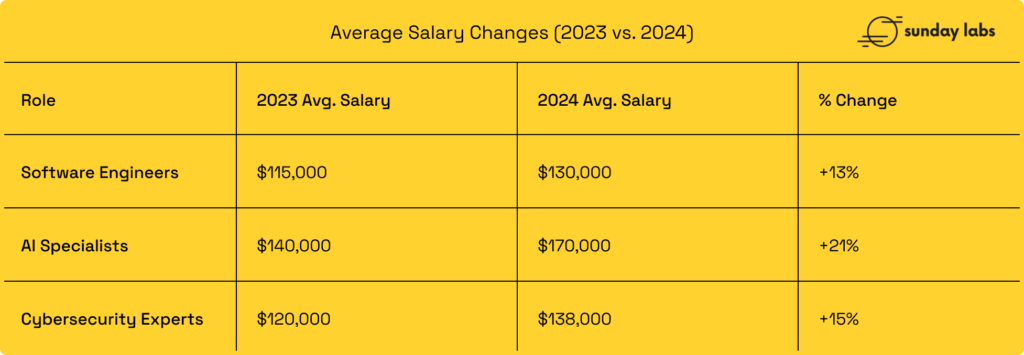
Average Salary Changes (2023 vs. 2024)
Key Learnings from 2024
- Premium for Niche Skills
Professionals with expertise in AI, machine learning, cybersecurity, and blockchain enjoyed higher salaries. Roles like MLOps engineers and blockchain developers saw up to a 30% increase in average compensation due to limited supply and high demand. - Regional Disparities Diminishing
The remote work culture further normalized in 2024, with companies offering comparable salaries regardless of location, particularly for top talent in high-demand areas. - Focus on Total Compensation
Companies increasingly used benefits like stock options, performance bonuses, and flexible work arrangements to attract and retain talent, shifting the focus from base pay to total rewards. - Retention Challenges
Rising salaries were coupled with high turnover rates as employees frequently moved for better opportunities. Companies responded by introducing retention bonuses and faster promotion cycles. - Entry-Level Pay on the Rise
Entry-level roles, especially in data science, software development, and DevOps, saw significant salary hikes as firms invested in grooming fresh talent.
Looking Ahead to 2025
- Sustained Growth in AI and Cybersecurity Pay
As AI adoption deepens and cyber threats increase, salaries for these roles are expected to grow further, with projected increases of 10-15% for specialized positions. - Demand for Cross-Functional Roles
Salaries for roles that blend technical and business expertise, such as AI product managers and tech-driven consultants, are likely to surge as companies seek strategic thinkers. - Pay Parity Initiatives
Companies are expected to strengthen pay parity efforts, closing gaps based on gender, ethnicity, and location, driven by employee advocacy and stricter regulations. - Focus on Upskilling Bonuses
Employers may incentivize skill development with upskilling stipends or bonuses, aligning employee growth with evolving organizational needs. - Global Market Adjustments
With tech companies hiring globally, salaries will see further standardization, and companies in emerging markets will need to stay competitive to retain local talent.
Final Conclusion
In 2024, tech hiring saw groundbreaking advancements with Generative AI, skills-first approaches, and remote work reshaping the landscape. However, challenges like widening skill gaps and ethical AI concerns persisted. The year highlighted the need for innovative yet ethical strategies to build a resilient, diverse, and future-ready workforce for 2025 and beyond.




